What is the VM0047 Methodology & How to Comply with It
Understanding Verra's VM0047 Methodology and How Treeconomy Can Help You Align with It
Project Development
Science & Tech
Apr 8, 2024
Carolina Amu Trujillo

Verra standards are a cornerstone for generating trust and validating impact in nature-based carbon removal projects. Last year, Verra introduced an improved methodology for Afforestation, Reforestation, and Revegetation (ARR) projects within the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) Programme. Designed to increase integrity in global carbon removal initiatives, this methodology, known as VM0047, represents a necessary evolution in the landscape of the voluntary carbon market.
In this blog, we dive into the VM0047 methodology and unveil our innovative assessment solution aligned with this standard (and more). We aim to empower project developers with the tools to evaluate their nature-based projects effectively.
Overview of VM0047
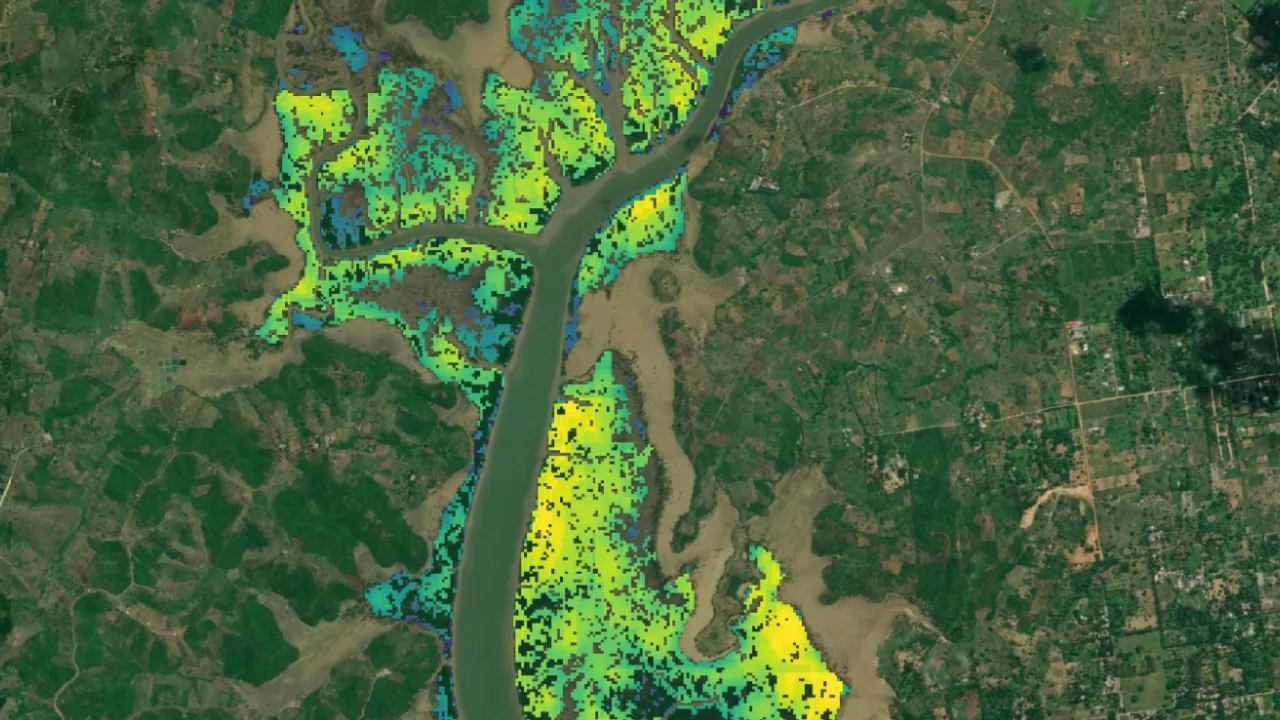
VM0047 is one of the latest Verra standards tailored for Afforestation, Reforestation, and Revegetation (ARR) carbon removal projects. Unlike earlier ARR standards with static baselines, VM0047 makes a significant leap forward by integrating dynamic performance benchmarks and leveraging remote sensing data to assess the additionality of projects. Through remote sensing and comparison with historically similar nearby land, VM0047 ensures that project interventions indeed lead to increased carbon sequestration beyond natural regeneration or business as usual.
At its core, VM0047 aims to quantify carbon removal from activities that enhance tree density or woody vegetation, offering two distinct quantification approaches:
Area-based Approach: This approach harnesses plot-based sampling and remote sensing-enabled dynamic performance benchmarks. By comparing biomass stocking changes between project areas and similar control plots, VM0047 facilitates the assessment of additionality and establishes crediting baselines at each verification stage.
Census-based Approach: Tailored for smaller projects where a comprehensive census of plantings is feasible, this approach focuses on dispersed planting activities. VM0047 establishes additionality by delineating project and alternative baseline scenarios, setting baselines at zero under conservative criteria.
Why is VM0047 necessary for nature-based projects?
The new VM0047 methodology is significant for nature-based projects for several reasons. First, it addresses the criticisms and challenges highlighted in previous methodologies, particularly regarding baseline selection.
One key feature of VM0047 is dynamic baselining, which allows for live and remote sensing-based comparisons. This robust baseline scenario enables a more accurate assessment of project additionality and performance. Furthermore, this methodology adheres to Verra standards and mirrors an emerging trend in the voluntary carbon market (VCM) towards leveraging satellite data to assess land performance and biomass changes. As this trend continues to evolve, integrating satellite data analysis into project assessments is poised to transition from an optional feature to a standard practice within the voluntary carbon market, representing a significant shift in approach.
In a broader context, the importance of VM0047 extends to the overall credibility and effectiveness of carbon credit markets. By addressing the imperfections of existing methodologies and improving the accuracy and transparency of nature-based carbon removal projects, VM0047 maintains the relevance and efficacy of carbon credit markets in combating climate change.
VM0047 key requirements
To comply with VM0047, projects must source up-to-date geospatial categorical data, including jurisdictional boundaries, ecoregion, policy environment, and land tenure. These data are essential for baseline construction and project validation, requiring updates at verification stages, typically every five years.
Treeconomy’s methodology involves the demarcation of project plots, the selection of representative control sites, and the calculation of stocking indexes, ensuring robust performance benchmarking.
Flexibility and accompanying module
VM0047 allows project developers to adopt either or both accounting approaches within their projects, provided that project areas do not overlap. Verra developed the VMD0054 Module for Estimating Leakage from ARR Activities to address leakage concerns, which is mandatory for projects utilising VM0047. This module enhances the accuracy and reliability of carbon offset projects by accounting for potential leakage.
Compliance with VM0047 is made simple with Treeconomy.
Most project developers seeking to adhere to VM0047 must conduct a performance benchmark at the project start and subsequent validation stages. Treeconomy offers an assessment solution that aligns seamlessly with this standard. Our assessment meticulously selects control sites outside the project boundary for benchmarking purposes. As the project progresses, the difference in a proxy of biomass and carbon between the project site and the selected control sites serves as a tangible demonstration of the intervention's additionality. This distinction directly influences the issuance and marketing of carbon removal credits.
Utilising satellite imagery and client-provided geospatial data (we have options available for customers who don’t have this. Feel free to ask us about them.), we provide comprehensive insights into the project’s impact. Our solution delivers essential outputs, including satellite base maps, carefully selected project and control plots, and performance benchmark values. This empowers project developers with actionable data for informed decision-making and instils confidence in their projects.
This assessment process is repeated with each credit verification to measure additionality and facilitate credit issuance accurately.
If you are a project developer interested in future-proofing and de-risking your projects, consider implementing our assessment. With it, you will go above and beyond the typical monitoring frequency to ensure thorough and accurate data collection in the long term.
How is the assessment done?
Our science and tech teams employ a meticulous assessment process to ensure that project developers meet the standards set by the VM0047 methodology and more.
Our robust assessment methodology is designed to provide clarity and precision in evaluating project performance and compliance. Let’s explore how we accomplish this:
1. Establishing the Performance Benchmark (PBt)
This dynamic value is a pivotal indicator, gauging the project's performance relative to historically similar land areas. It quantifies the impact of interventions on the site over time, influencing credit allocation.
2. Implementing the Assessment Step by Step
Site Division: The project site is divided into equal-area squares (project plots), with a minimum of 30 squares randomly selected.

Categorical Summaries: We precisely gather categorical summaries of project plots, including jurisdiction, ecoregion, policy environment, and land tenure, among others.

Matching Characteristics: Leveraging the 'donor pool,' we identify surrounding land areas that match the categorical variables of the project site within a defined radius.

Stocking Index Evaluation: Before analysing stocking indices, we assess proxies of ground biomass to understand vegetation health and distribution.
Satellite Imagery Retrieval: We retrieve multispectral satellite imagery, such as LANDSAT and Sentinel datasets, to construct stocking indices.
Building Stocking Indices: Five stocking indices, including NDVI, EVI, LAI, TRVI, and NDFI, are selected and tested. These indices provide crucial insights into vegetation health and biomass distribution.

Biomass Data Collection: We use GEDI, a NASA-operated LiDAR instrument on the ISS, to gather detailed aboveground biomass density (AGBD) data, essential for understanding vegetation structure.
Establishing Relationships: Through rigorous analysis, we establish relationships between stocking indices and biomass measurements, aiding in the prediction of biomass distribution.
Predictive Modelling: We use established relationships to predict biomass distribution across project areas.
3. Calculating project values and matching
NDFI emerges as our preferred stocking index due to its correlation with biomass and carbon levels, which is crucial for compliance assessment.

Utilising NDFI: NDFI serves as a proxy for biomass and carbon, enabling the calculation of values for project plots and the donor pool.
Matching Process: We employ a k-nearest neighbour matching based on a multivariate distance metric to ensure fair and accurate matching.


4. Validating Compliance
Scoring Against Covariates: We validate compliance by scoring matching against covariates, ensuring fairness and accuracy in the assessment process.
We calculate the standardised difference of means, and if it is below 0.25 for our choice of project plots and control plots, we’re good to proceed.
Marketable credits: The performance benchmark is calculated once we have post-intervention data. This affects how many credits are additional and, therefore, can be marketed
Our commitment is to provide our customers the highest precision and reliability, hence why our assessment methodology continues to undergo refinement and optimisation.
Get your project in check with us.
Verra standards such as VM0047 represent a significant step forward in enhancing credibility on the impact of nature-based carbon removal projects. Treeconomy’s assessment solution, aligned with VM0047, ensures compliance and provides valuable insights into project impacts. We are ready to assist project developers seeking to assess their nature-based projects.
Contact our commercial team to learn more and take the next step toward achieving your project goal.